ald in babies definition
As a result levels of these fatty acids build up in the brain and nervous system preventing nerve cells from sending signals to the body. Furthermore through ALD Newborn Screening affected children have the opportunity to benefit from lifesaving treatment which can halt the disease see Treatment Section.
Adrenoleukodystrophy ALD occurs when certain fats very long chain fatty acids or VLCFAs cannot be broken down in the body.

. It affects the nervous system and adrenal glands. The sex chromosomes however are. Adrenoleukodystrophy ALD is a rare genetic condition that causes the buildup of very long chain fatty acids VLCFAs in the brain.
This disease largely affects the nervous system and adrenal glands. Genes usually come in pairs with each parent giving one copy to their child. Adrenoleukodystrophy or ALD is an x-linked metabolic disorder characterized by progressive neurologic deterioration due to demyelination of the cerebral white matter.
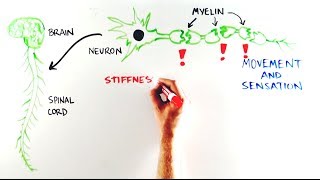
ALD involves multiple organs in the body but most prominently affects the brain and spinal cord. Steroids can be used to. Without the myelin sheath the nerves can no longer relay information to and from the brain.
Forms of X-linked ALD include. Symptoms of ALD often include behavioral and cognitive changes. It was first recognized in 1923 and has also been known as Schilders disease and sudanophilic leukodystrophy.
Adrenoleukodystrophy or ALD is a deadly genetic disease that affects 1 in 17000 people. Without that sheath the neurons cannot. It is an X-linked genetic disease therefore it mostly affects boys and men.
The basic adrenoleukodystrophy definition 1 is a genetic disorder that causes damage to nerve fibers in the brain. Because boys only have one copy of the gene when it is mutated they become susceptible to ALD. In those babies X-ALD is not inherited from a parent.
Myelin acts as insulation around the nerve fibers. ALD mostly affects children. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy X-ALD is an inherited genetic condition that prevents the body from breaking down certain fats.
Adrenoleukodystrophy ALD is an inherited condition caused by a faulty gene. Adrenoleukodystrophy ALD is one of a group of genetic disorders called the leukodystrophies that cause damage to the myelin sheath of the nerve fibers in the brain. This may be an option to slow or halt the progression of adrenoleukodystrophy in children if ALD is diagnosed and treated early.
Girls inherit two X chromosomes one from each parent. Adrenoleukodystrophy ALD is a genetic condition that damages the membrane myelin sheath that covers nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. Children with suspected ALD may need additional testing including vision screens.
Treatment focuses on stopping or slowing the diseases progression and improving symptoms. ALD involves multiple organs in the body so it most prominently affects the brain. The white matter of the brain is progressively damaged.
ALD Adrenoleukodystrophy Adrenoleukodystrophy ALD is a genetic disorder connected to the X chromosome. Adrenoleukodystrophy or ALD is a deadly genetic disease that affects 1 in 17000 people. Not being able to get or keep an erection.
Adults can experience symptoms and develop a form of the disease as well but. It is an X-linked genetic disease which means it most severely affects boys and men. The classic childhood form which is the most severe and affects only boys may occur between ages 4.
These fats build up and affect how the body normally functions. In this type of inheritance the gene associated with the condition in X-ALD the gene ACBD1 is located on the X chromosome one of the sex chromosomes. In children with ALD the body cannot break down certain fatty acids which are the building blocks of fat.
When VLCFAs accumulate they destroy the protective myelin sheath around nerve cells responsible for brain function. Many people who have ALD develop adrenal insufficiency and. Brain function declines as the protective myelin sheath is gradually stripped from the brains nerve cells.
Adrenoleukodystrophy or ALD is a genetic disease that affects 1 in 17000 people. Adrenoleukodystrophy ALD is a disease linked to the X chromosomeIt is a result of fatty acid buildup caused by a defect in the very long chain of fatty acids transporter in peroxisomes which then causes damage to the myelin sheath of the nerves resulting in seizures and hyperactivity. Other symptoms include problems with speaking listening and understanding verbal.
Treatment methods depend on the type of ALD you have. This form of X-linked ALD usually occurs between ages 4 and 10. ALD affects males more than females.
Adrenoleukodystrophy Adult with Learning Difficulties Medspeak-UK alcoholic liver disease aldosterone anterior latissimus dorsi approximate lethal dose arithmetic learning disorder aspirin-like drug assistive listening. Feeling an urgent need to pee or poop. In the 1970s the name adrenoleukodystrophy was.
Childhood adrenoleukodystrophy is the first and most common cause though ALD disease in adults is possible. Peroxisomes are small areas inside your cells that perform. Numbness or tingling in the legs.
This brain disorder destroys myelin the protective sheath that. Adrenoleukodystrophy ALD is a serious progressive genetic disorder that affects the adrenal glands the spinal cord and the white matter myelin of the nervous system. The functional copy inherited from dad usually protects female children from the disease.
The myelin sheath is a fatty covering which acts as an electrical insulator. Treatment options may include. This makes it impossible for nerves in the body to communicate with the brain.
Adrenoleukodystrophy is a rare genetic disorder in which the body cannot break down fatty acids in the brain. As it is an X-linked genetic disease which means it most severely affects boys and men. When this insolating layer is damaged nerve signals from the brain cannot communicate across the body properly causing impaired bodily functions or.
When an individual has ALD the buildup of VLCFAs may disrupt. The resulting buildup of fatty acids leads to a breakdown of the myelin sheath the insulation covering that protects the nerve fibers in the brain. Stem cells may be taken from bone marrow through bone marrow transplant.
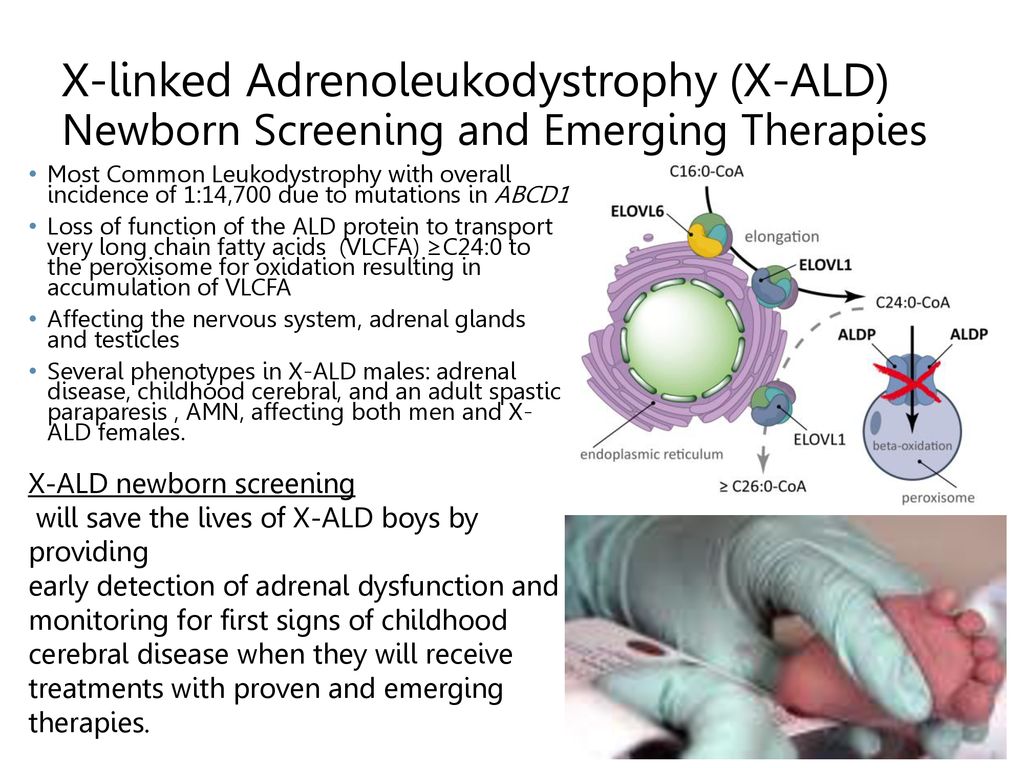
The X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy protein ALDP is a transporter protein that brings a type of fat called very long-chain fatty acids VLCFA into peroxisomes to be processed. The most common type of ALD is X-linked ALD which is caused by a genetic defect on the X chromosomeX-linked ALD affects males more severely than females who carry the disease.
Adrenoleukodystrophy Ald Johns Hopkins Medicine

Children Testing Positive For X Ald On Updated Newborn Screening Panels Require Long Term Monitoring Pediatrics Nationwide

Cerebral Adrenoleukodystrophy Child Neurology Foundation

Cerebral Adrenoleukodystrophy Child Neurology Foundation
X Ald Newborn Screening And Follow Up Testing In Usa Ppt Download

Adrenoleukodystrophy Disease Ald Causes Treatment Symptoms Hunter S Hope

Treatments For Epilepsy Parents